When shopping for a new TV, you may come across several different acronyms and technical terms that can be confusing. OLED, QLED, and MicroLED are all types of display technologies that are popular in high-end TVs. Each technology has its own strengths and weaknesses, so it’s important to understand the differences between them before making a purchasing decision.
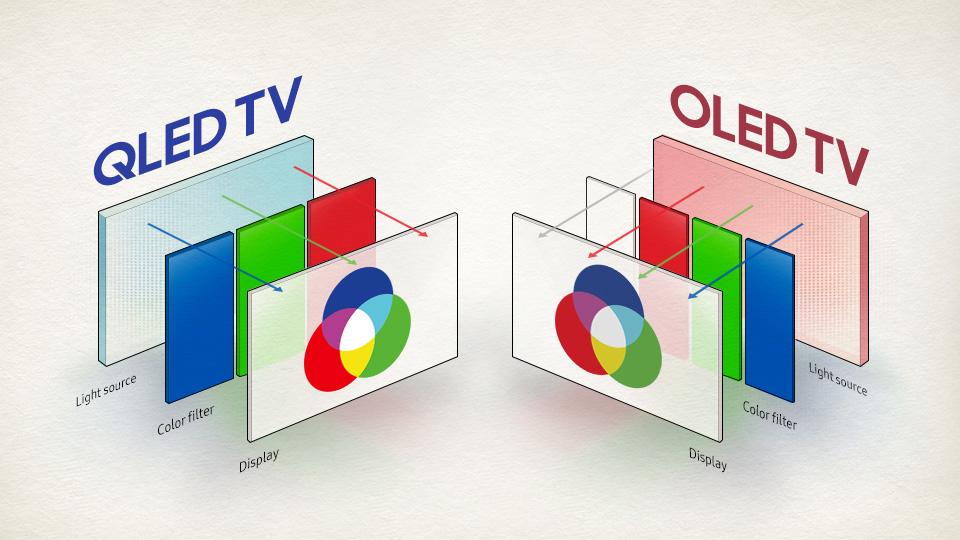
OLED
Let’s start with OLED – OLED stands for “Organic Light Emitting Diode.” In an OLED display, each individual pixel emits its own light, allowing for true black levels and excellent contrast. This means that when a pixel is supposed to be black, it is actually turned off, resulting in perfect blacks that are unmatched by any other display technology.
OLED displays are also known for their wide viewing angles, which means that the picture quality remains consistent no matter where you’re sitting. This is because OLED pixels emit light directly, rather than relying on a backlight like LCD displays.
One potential downside of OLED displays is that they can suffer from “burn-in,” where a static image is displayed for too long, causing the pixels to age unevenly. However, this is becoming less of a concern with newer OLED panels.
Related: Here’s why you shouldn’t buy a 8K TV in 2023
QLED
QLED stands for “Quantum Light Emitting Diode.” QLED displays use quantum dots, which are tiny particles that emit light when stimulated by an electric current. In a QLED display, a backlight shines through a layer of quantum dots to create the colors on the screen.
One of the biggest advantages of QLED displays is their brightness. Because they use a backlight, QLED displays can get much brighter than OLED displays, which can be beneficial for watching HDR content in a brightly lit room.
However, QLED displays can suffer from blooming, which is when bright objects on the screen bleed into dark areas, resulting in a halo effect. They also have more limited viewing angles than OLED displays.
MicroLED
MicroLED stands for “Micro Light Emitting Diode.” MicroLED displays are similar to OLED displays in that each pixel emits its own light, but they use inorganic materials instead of organic ones.
One of the biggest advantages of MicroLED displays is their modularity. Because each pixel is its own light source, MicroLED displays can be made in any size or shape, and can be combined to create displays of almost any size.
MicroLED displays also have excellent contrast and black levels, similar to OLED displays. They do not suffer from burn-in like OLED displays do, and they have very fast response times.
However, MicroLED displays are currently very expensive to produce, which makes them prohibitively expensive for most consumers. They also have more limited color gamuts than OLED or QLED displays, although this may improve as the technology advances.
So which to choose?
When it comes to choosing between OLED, QLED, and MicroLED displays, there is no clear winner. Each technology has its own strengths and weaknesses, and the best choice for you will depend on your specific needs and preferences.
OLED displays are great for watching movies and TV shows in a dark room, and for people who prioritize perfect black levels and wide viewing angles.
QLED displays are great for watching HDR content in a bright room, and for people who prioritize brightness and vivid colors. For more information about QLED, check out Samsung’s page dedicated to QLED: What is a QLED TV?
MicroLED displays are currently the most cutting-edge technology, and are great for people who want a truly custom display or who need the fastest response times. However, they are also the most expensive and currently have limited availability.